The documentation from version 39.5.17 of PLANTA project can be found in the new PLANTA Online Help .
.
Relations and Customizing of Structures
Note- Customizing of structures must not be confused with customizing of structure displays.
- For structure display customizing, see
Relational Structures (Structures by Relations)
Information- Via relations, logical relations between data are established.
- Relations can be defined in data tables or in modules.
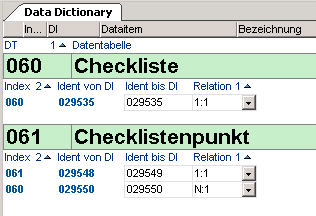
Relations in Data Tables
Information- Data tables can be linked via relations.
- The relations are defined per data table in the Data Dictionary module with the Relationship parameters of DT416.
- The Checklist data table 060 and Checklist item 061 are linked via a N:1 relation.
- I.e. several checklist items can be assigned to each checklist but each checklist item only belongs to one checklist.
- The checklist item data table is subordinate to the checklist data table.
Relations in Modules (Data Area Assignment)
Information- In a module, data from different data tables that have no data table relation, e.g. DT461 Project and DT467 Resource, can be displayed linked and structured.
- Create the data areas from different data tables and assign them to the required module.
- Structure data areas (connect relationally):
- Insert the relation to the parent area for the child data area in the Relation to parent area parameter.
- With relations, data tables that contain application logic interrelated data items, can be linked. The project manager (DT461) can, e.g., be linked to the resource (DT467) but not to the cost type (DT470).
Recursive Structures
From 39
Information
- One speaks of recursive structures (also recursive relation) if data of a data table possess a hierarchical relation to other data of the same data table.
- This can be done via the Recursive relation parameter
- Task (DT463)
- Subtask (DT463)
Up to DB 39
Information
- One speaks of recursive structures (also recursive relation) if data of a data table possess a hierarchical relation to other data of the same data table.
- This can be done via a special structure data table or via the Recursive Relation parameter.
- Via a structure data table
- Resource (DT467)
- Child resource (DT469)
- Resource (DT467)
- Via the Recursive Relation parameter
- Task (DT463)
- Subtask (DT463)
- Task (DT463)
Structuring via Structure Data Table
From 39
In Releases 39, PLANTA no longer uses structure data tables.
Up to DB 39
Information
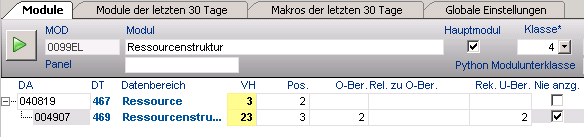
- Object and structure data are available in different data tables and there is a data base relation between them (e.g. DT467 Resource and DT469 Resource Structure).
- Data areas
- Object data area DT467: the data in this data area are to be displayed in a structured way.
- Structure data area DT469: the data in this area contain the structure information (which child resources a resource has).
- Module
- Object data area is the parent data area of structure data area.
- Enter the the position of the object data area in the structure data area in the recursive child area parameter (recursive child area) and activate the Never display parameter.
- Customizing of a resource structure
- Results in the module
Attention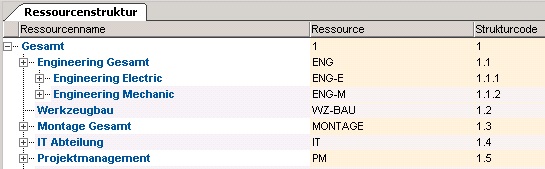
- The structure is only displayed if the Tree data area parameter is set to 1.
Structuring via Recursive Relation
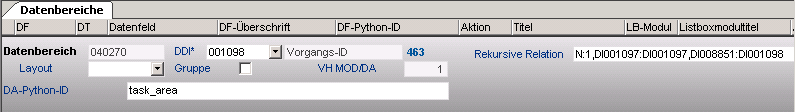
Information- Object and object structure data are contained in the same data table (e.g. task and parent task: both DT463).
- Data area
- In this case, the relation between the object and its subobjects is achieved via the relationship entry in the Recursive Relation field.
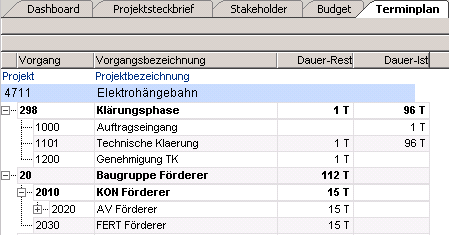
- Relation entry in the Task data area of the Schedule module for structuring the tasks
- Results in the module
Note
- The function, that the width of the first field was automatically extended (in this case the fields of the task ID), only applies to data areas with horizontal layout.
| I | Attachment | History | Size | Date | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
CURessStruktur.png | r1 | 8.0 K | 2010-11-04 - 11:59 | |
| |
CUVGStruktur.png | r1 | 7.2 K | 2010-11-04 - 12:50 | |
| |
DTRelation.png | r1 | 6.4 K | 2010-11-04 - 11:45 | |
| |
ErgebnisRessStruktur.png | r1 | 6.9 K | 2010-11-04 - 12:00 | |
| |
ErgebnisVGStruktur.png | r1 | 9.2 K | 2010-11-04 - 12:49 | |
| |
Struktur.png | r1 | 4.6 K | 2010-11-02 - 14:33 |