Die Dokumentation ab Version 39.5.17 von PLANTA project finden Sie in der neuen PLANTA Online-Hilfe .
.
Jython API
Information- This topic describes the public Jython API of PLANTA
- These functions are guaranteed to be supported in future versions
- When you have enabled the planta link web services you can reload your jython code by saving in the module Web-Schnittstellen
- This invokes a clearing of the jython cache and resets the imported modules
Quickstart
Information- The Jython code resides under
<server folder>/jython - The Jython version is 2.7, which can be quite different from 3.6 which you use in regular customizing
- The Jython interpreter is embedded in the Java part of the project Server instead of the native c part
- This means you have no access to the regular Python API (everything under
<server folder>/py) - Instead you have access to the Jython API (everything under
<server folder>/jython), the Java API and small parts of the project Server Java API
- This means you have no access to the regular Python API (everything under
- At the time of writing there is no way to access the GUI from Jython, so you can't interact with panels, modules, datafields, or anything like that (Not even message boxes)
- You don't work with dtp or mts records, instead you operatore with the same POJOs (Plain Old Java Object) that the project Server works with
- Currently there are 2 places where Jython code can be executed from: When calling a PLANTA link web interface or when an event with a Jython function is triggered
- Every table in project that has a valid Universally Unique IDentifier DI gets turned into a POJO
- The Entitätsbezeichnung determines the class name of the object
- The customizing.utilities package has all basic functions you need to interact with POJOs
- The object protection fields (Creation user, changed date, ...) are not set automatically, you have to manually call set_object_protection_fields from
customizing.utilitieswhen you want to set the object protection fields - All dataitems where Virtuell =
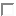 are loaded as attributes of the POJO and can be read or written, virtual dataitems don't exist in the POJO world
are loaded as attributes of the POJO and can be read or written, virtual dataitems don't exist in the POJO world
- When you are working with data that is beyond the realm of plain ascii you need to use the Python 2.7 unicode string notation
u'Exämple' - You need to be especially careful when you write logging messages that write out user input data and turn the entire message into an unicode string like this:
logger.debug(u'Query: "{}"'.format(self.query))
Logging
You can use logging calls to debug your Jython code.- Depending on what context the code is run in the logging is written to different places:
- If the code is executed from an event the logging is written to the
Event.logfile - If the code is executed from a web interface the logging is written to the web interface logging table and can be viewed in the PLANTA link web logging modules
- If the code is executed from an event the logging is written to the
- If a web interface performs an operation that triggers an event the event log is written to both
Event.logand the web interface log
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def custom_event(event):
logger.info('Custom event was called!')
# .../jython/ folder, so both /customizing/ and /server/ packages can log, but also individual customer packages
Customizing API
utilities
Theutilities package provides various helper functions.
Tip - Avoid importing any functions from their absolute namespace and instead use the
utilitiesnamespace - This ensures your code will stay compatible with future releases
#from customizing.utilities.database import db_select Don't do this! from customizing import utilities # Do this! utilities.db_select(query)
| Namespace | Topic |
|---|---|
| utilities.cache | Caching expensive function calculations |
| utilities.customizer | Functions for getting text constants, global settings and listbox categories/values |
| utilities.data | Various business logic functions |
| utilities.database | Functions for interacting with the database |
| utilities.enums | Various Enums |
| utilities.exception | Custom Exceptions |
| utilities.pojo | Functions for interacting with POJOs |
| utilities.send_email | Classes for sending emails from Jython |
