The documentation from version 39.5.17 of PLANTA project can be found in the new PLANTA Online Help .
.
Universal Interface (PLANTA link)
From DB 39.5.10
In DB version 39.5.9, some modules of the universal interface have been revised and the user menu has been restructured. For this purpose, some modules have been replaced and some have been added. For more information, see the PLANTA link table of contents.
General
Information- The universal interface (PLANTA link) is the basis for using arbitrary interfaces in PLANTA.
- On this basis, individual solutions can be realized that meet the specific demands of each customer in terms of data transfer extent and structure. Some predefined interface templates are already contained in the scope of supply of the PLANTA software (provided that the PLANTA link component has been licensed).
- The graphical interface of PLANTA link permits the simple creation, configuration, and visualization of interfaces. Intermediate steps for data conversion, checkup, or processing can be considered in this.
- PLANTA link supports different types of import/export data provision and reception, a.o. file formats (.csv, …), web service, and SAP RFC calls. As a result, both the mapping of the interface as well as the way in which data is made available can be adjusted independent of one another.
- The interfaces can be parameterized and automated.
- The following description provides you with an overview of the functions of the Universal Interface. For detailed information, please consider the links that will lead you to further topics of the table of contents of the complete interface documentation, which can be found at the bottom of this topic.
Prerequisites
Attention- In order to use the Universal Interface, you have to license the PLANTA link
 add-on.
add-on. - If you have any questions, please contact your PLANTA consultant.
- PLANTA link role 01100028 must be assigned to the respective user.
- You do not need customizer rights to run this transfer and to adapt parameters. However, you do need customizer rights to create new transfer modules.
- Several modules that guarantee access to customizing records are only available in read mode if you do not have customizer rights.
- When exporting the files in PLANTA link, you have to note the following:
- Linux: Every user of the "others" group has read and write rights for the export files.
- Windows: The export files inherit the security settings from the folder in which they have been stored (files).
Terminology
Information- Source
- is a source module in which records are provided for the transfer
- Target
- is a target module that receives the records
- Pool
- is a pool module in which data can be saved temporarily
- It is not necessary to use the pool module and the pool tables. This is only required if either data in the pool is to be re-edited or the data set at the time of export is to be traceable in the future. Pool tables can also be used to prepare data from an external system before it will finally be written in PLANTA. In the Standard, PLANTA provides three pool tables: DT563 Load data pool, DT566 Employee pool, NEW DT567 Project pool. If other data is imported/export by the customer via pools, you have to create the corresponding data tables.
- is a pool module in which data can be saved temporarily
- Configuration
- contains the key data of an interface and represents the parent interface object.
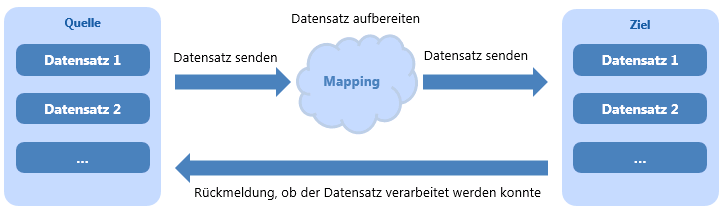
- Mapping
- Specifies which columns in the source correspond to which columns in the target
- Additionally, a mapping allows to check, convert, and adapt values before they are sent to the target module.
- A mapping always leads from a source to a target. Between source and target, various mapping functions can be interposed.
Procedure
Schematic displayRelevant Modules
Interface Configuration
Configuration
Information- In the Configuration module, interfaces can be configured.
- In the configuration, source and target (or a pool) are defined and the mapping is generated.
- PLANTA provides several predefined configuration templates.
Execution
Information- In the Execution module, a configuration is run, i.e. the data is transfered from source to target and all defined mapping functions are run.
- Simultaneously, there is a report to the source module on whether records could have been processed (in the form of log entries in the Logging module).
Interface Administration
Information- In the Open Configurations module, configurations that are not executed yet are listed. Here, they can be set to Completed, be deleted, opened manually, and run.
- In the Completed Configurations module NEW, archived configurations can be viewed.
Special Functions
Information- The Generate Interface Definition module enables you to transfer the interface mapping elements to an Excel file in order to check the properties of individual elements, e.g. DF length, formats, etc.
- The Systems module enables you to define the interface behavior for different systems.
- The Extended Configuration Options module provides an overview of all existing interface configurations with the option to define for each configuration whether it is to be hidden or locked.
- NEW The Fast Creation of Employee Data module enables you to create employee data centrally and subsequently import it to all relevant data tables.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages and disadvantages of an interface with/without pool?
- In the interface pool, transfer data is cached before it is sent to its target.
- In direct transfer without pool, the source must always be cleaned up directly for invalid records that could not be received. This can be, e.g., the adjustment of lines of a csv file, or the direct editing of the lines in an ERP system. For large source files, it may make sense to remove already transferred records from the data volume of the source.
- The pool enables you to load the data without larger validation steps, which results in the data being directly available in PLANTA and the original source no longer being required for further processing.
- In the pool, data can be edited directly with the help of a direct module if necessary, which is often more comfortable than editing the data in the CSV file or in ERP itself.
- The pool also serves as a type of archive for the data that has been sent initially from the source before they were received via transformation rules.
- The pool table can be used to customize overview modules that show which records could not be processed by the interface with possible direct editing function for correcting the data and initiating the interface again.
From DB 39.5.9
In DB version 39.5.9, some modules of the universal interface have been revised and the user menu has been restructured. For this purpose, some modules have been replaced and some have been added. For more information, see the PLANTA link table of contents.
General
Information- The universal interface (PLANTA link) is the basis for using arbitrary interfaces in PLANTA.
- On this basis, individual solutions can be realized that meet the specific demands of each customer in terms of data transfer extent and structure. PLANTA already provides several predefined interface templates.
- The graphical interface of PLANTA link allows easy creation, configuration, and visualization of interfaces. Intermediate steps for data conversion, checkup, or processing can be considered.
- PLANTA link supports different types of import/export data provision and reception, a.o. file formats (.csv, …), web service, and SAP RFC calls. As a result, both the mapping of the interface as well as the way in which data is made available can be adjusted independent of one another.
- The interfaces can be parameterized and automated.
- The following description provides you with an overview of the functions of the Universal Interface. For detailed information, please consider the links that will lead you to further topics of the table of contents of the complete interface documentation, which can be found at the bottom of this topic.
Conditions of Use
Attention- In order to use the Universal Interface, you have to license the PLANTA link
 add-on.
add-on. - If you have any questions, please contact your PLANTA consultant.
- PLANTA link role 01100028 must be assigned to the respective user.
- You do not need customizer rights to run this transfer and to adapt parameters. However, you do need customizer rights to create new transfer modules.
- Several modules that guarantee access to customizing records are only available in read mode if you do not have customizer rights.
- When exporting the files in PLANTA link, you have to note the following:
- Linux: Every user of the "others" group has read and write rights for the export files.
- Windows: The export files inherit the security settings from the folder in which they have been stored (files).
Terminology
Information- Source
- is a source module in which records are provided for the transfer
- Target
- is a target module that receives the records
- Pool
- is a pool module in which data can be saved temporarily
- It is not necessary to use the pool module and the pool tables. This is only required if either data in the pool is to be re-edited or the data set at the time of export is to be traceable in the future. Pool tables can also be used to prepare data from an external system before it will finally be written in PLANTA. In the Standard, PLANTA provides 2 pool tables: DT563 Load data pool, DT566 Employee pool, NEW DT567 Project pool. If other data is imported/export by the customer via pools, you have to create the corresponding data tables.
- is a pool module in which data can be saved temporarily
- Configuration
- A configuration considers the key information of an interface and represents the parent interface object.
- Mapping
- Specifies which columns in the source correspond to which columns in the target
- Additionally, a mapping allows to check, convert, and adapt values before they are sent to the target module.
- A mapping always leads from a source to a target. Between source and target, various mapping functions can be interposed.
Procedure
Schematic displayRelevant Modules
Interface Configuration
Configuration
Information- In the Configuration module, interfaces can be configured.
- In the configuration, source and target (or a pool) are defined and the mapping is generated.
- PLANTA delivers several predefined configuration templates.
Execution
Information- In the Execution module, a configuration is run, i.e. the data is transfered from source to target and all defined mapping functions are run.
- Simultaneously, there is a report to the source module on whether records could have been processed (in the form of log entries in the Logging module).
Interface Administration
Information- In the Open Configurations module NEW, configurations that are not executed yet are listed. Here, they can be manually set to Completed, be deleted, or opened and run.
- In the Completed Configurations module NEW, archived configurations can be viewed.
Special functions NEW
Information- The Generate Definition module NEW enables you to transfer the interface mapping elements in an Excel file in order to check the properties of individual elements, e.g. DF length, formats, etc.
- The Systems module enables you to define the interface behavior for different systems.
- The Extended Configuration Options module provides an overview of all existing interface configurations with the option to define for each configuration whether it is to be hidden or locked.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages and disadvantages of an interface with/without pool?
- In the interface pool, transfer data is cached before it is sent to its target.
- In direct transfer without pool, the source must always be cleaned up directly for invalid records that could not be received. This can be, e.g., the adjustment of lines of a csv file, or the direct editing of the lines in an ERP system. For large source files, it may make sense to remove already transferred records from the data volume of the source.
- The pool enables you to load the data without larger validation steps, which results in the data being directly available in PLANTA and the original source no longer being required for further processing.
- In the pool, data can be edited directly with the help of a direct module if necessary, which is often more comfortable than editing the data in the CSV file or in ERP itself.
- The pool also serves as a type of archive for the data that has been sent initially from the source before they were received via transformation rules.
- The pool table can be used to customize overview modules that show which records could not be processed by the interface with possible direct editing function for correcting the data and initiating the interface again.
From DB 39.5.7
In DB version 39.5.7, the universal interface has been strongly edited and designed more user-friendly. For this purpose, some modules have been replaced and some have been added. For more information, see the PLANTA link table of contents.
General
Information- The universal interface (PLANTA link) is the basis for using arbitrary interfaces in PLANTA.
- On this basis, individual solutions can be realized that meet the specific demands of each customer in terms of data transfer extent and structure. PLANTA already provides several predefined interface templates.
- The graphical interface of PLANTA link allows easy creation, configuration, and visualization of interfaces. Intermediate steps for data conversion, checkup, or processing can be considered.
- PLANTA link supports different types of import/export data provision and reception, a.o. file formats (.csv, …), web service, and SAP RFC calls. As a result, both the mapping of the interface as well as the way in which data is made available can be adjusted independent of one another.
- The interfaces can be parameterized and automated.
- The following description provides you with an overview of the functions of the Universal Interface. For detailed information, please consider the links that will lead you to further topics of the table of contents of the complete interface documentation, which can be found at the bottom of this topic.
Conditions of Use
Attention- In order to use the Universal Interface, you have to license the PLANTA link
 add-on.
add-on. - If you have any questions, please contact your PLANTA consultant.
- PLANTA link role 01100028 must be assigned to the respective user.
- You do not need customizer rights to run this transfer and to adapt parameters. However, you do need customizer rights to create new transfer modules.
- Several modules that guarantee access to customizing records are only available in read mode if you do not have customizer rights.
- When exporting the files in PLANTA link, you have to note the following:
- Linux: Every user of the "others" group has read and write rights for the export files.
- Windows: The export files inherit the security settings from the folder in which they have been stored (files).
Terminology
Information- Source
- is a source module in which records are provided for the transfer
- Target
- is a target module that receives the records
- Pool
- is a pool module in which data can be saved temporarily
- It is not necessary to use the pool module and the pool tables. This is only required if either data in the pool is to be re-edited or the data set at the time of export is to be traceable in the future. Pool tables can also be used to prepare data from an external system before it will finally be written in PLANTA. In the Standard, PLANTA provides 2 pool tables: DT563 Load data pool, DT566 Employee pool, NEW DT567 Project pool. If other data is imported/export by the customer via pools, you have to create the corresponding data tables.
- is a pool module in which data can be saved temporarily
- Configuration
- A configuration considers the key information of an interface and represents the parent interface object.
- Mapping
- Specifies which columns in the source correspond to which columns in the target
- Additionally, a mapping allows to check, convert, and adapt values before they are sent to the target module.
- A mapping always leads from a source to a target. Between source and target, various mapping functions can be interposed.
Procedure
Schematic displayRelevant Modules
Configuration
Information- In the Configuration module, interfaces can be configured.
- In the configuration, source and target (or a pool) are defined and the mapping is generated.
- PLANTA delivers several predefined configuration templates.
Execution
Information- In the Execution module, a configuration is run, i.e. the data is transfered from source to target and all defined mapping functions are run.
- Simultaneously, there is a report to the source module on whether records could have been processed (in the form of log entries in the Logging module).
Archive
Information- In the Archive (MOD009CIP) module, archived configurations can be viewed.
- In the Open Transactions module, configurations are listed that are not executed yet. Here, they can be manually set to Transferred, be deleted, or opened and run.
Administration
Information- The Generate Definition module enables you to transfer the interface mapping elements in an Excel file in order to check the properties of individual elements, e.g. DF length, formats, etc.
- The Systems module enables you to define the interface behavior for different systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages and disadvantages of an interface with/without pool?
- In the interface pool, transfer data is cached before it is sent to its target.
- In direct transfer without pool, the source must always be cleaned up directly for invalid records that could not be received. This can be, e.g., the adjustment of lines of a csv file, or the direct editing of the lines in an ERP system. For large source files, it may make sense to remove already transferred records from the data volume of the source.
- The pool enables you to load the data without larger validation steps, which results in the data being directly available in PLANTA and the original source no longer being required for further processing.
- In the pool, data can be edited directly with the help of a direct module if necessary, which is often more comfortable than editing the data in the CSV file or in ERP itself.
- The pool also serves as a type of archive for the data that has been sent initially from the source before they were received via transformation rules.
- The pool table can be used to customize overview modules that show which records could not be processed by the interface with possible direct editing function for correcting the data and initiating the interface again.
From S 39.5.4 to DB 39.5.7
Attention
- From server version 39.5.4, PLANTA provides the Universal Interface ((PLANTA link) replacing the previous ERP interface.
- In order to use the universal interface, the PLANTA link
 add-on must be licensed.
add-on must be licensed. - If you have any questions, please contact your PLANTA consultant.
- The universal interface (PLANTA link) is the basis for using arbitrary interfaces in PLANTA.
- On this basis, individual solutions can be realized that meet the specific demands of each customer in terms of data transfer extent and structure. PLANTA already provides several predefined interface templates.
- The following description provides you with a rough, general overview of the functions of the Universal Interface. For detailed information, please consider the links that will lead you to further topics of the table of contents of the complete interface documentation, which can be found at the bottom of this topic.
Conditions of Use
Information- Work area 01100166 PLANTA link must be assigned to the required user (either integrate in one of the existing roles or create a new role and assign the work area).
- You do not need customizer rights to run this transfer and to adapt parameters. However, you do need customizer rights to create new transfer modules.
- Several modules that guarantee access to customizing records are only available in read mode if you do not have customizer rights.
Procedure
Schematic displayConfiguration
Information- In the Configuration module, interfaces can be configured.
- A configuration considers the key information of an interface and represents the parent interface object.
- In the configuration, source and target (or a pool) are defined and the mapping is generated.
- Source
- is a source module in which records are provided for the transfer
- Target
- is a target module that receives the records
- Pool
- is a pool module in which data can be saved temporarily
- It is not necessary to use the pool module and the pool tables. This is only required if either data in the pool is to be re-edited or the data set at the time of export is to be traceable in the future. Pool tables can also be used to prepare data from an external system before it will finally be written in PLANTA. In the Standard, PLANTA provides 2 pool tables: DT 563 Load data pool, DT 566 Employee pool. If other data is imported/export by the customer via pools, you have to create the corresponding data tables.
- is a pool module in which data can be saved temporarily
- Mapping
- Specifies which columns in the source correspond to which columns in the target
- Additionally, a mapping allows to check, convert, and adapt values before they are sent to the target module.
- A mapping always leads from a source to a target. Between source and target, various mapping functions can be interposed.
- PLANTA delivers several predefined configuration templates.
Transaction
Information- In the Transaction module, a configuration is run, i.e. data is transferred from source to target and all mapping functions are run.
- Simultaneously, there is a report to the source module on whether records could have been processed (in the form of log entries in the Logging module).
Archive
Information- In the Archive (MOD009C64) module, archived configurations can be viewed.
See also:
From DB 39.5.16
General
Workflows (Tutorials)
- Interface Workflow: Export
- Interface Workflow: Import
- Web Interface Workflow: GET
- Web Interface Workflow: PUT
- Web Interface Workflow: POST
- Web Interface Workflow: DELETE
- DT560 Interface Configuration
- DT561 Configuration Parameters
- DT562 Mapping
- DT563 Load Data Pool
- DT564 Logging
- DT565 Mapping Parameters
- DT566 Employee Pool
- DT567 Project pool
- DT568 System
- DT569 System condition
- DT590 Web interface
- DT592 Web entity
- DT593 Web attribute
- DT594 Web parameter
- DT595 Web request
From DB 39.5.15
General
Workflows (Tutorials)
- Interface Workflow: Export
- Interface Workflow: Import
- Web Interface Workflow: GET
- Web Interface Workflow: PUT
- Web Interface Workflow: POST
- Web Interface Workflow: DELETE
- Interface Configuration
- Configuration and Execution panel
- Interface Administration
- Special Functions
- Web interfaces
- PLANTA pulse interfaces
- Jira Interfaces NEW
- Configuration panel NEW
- User Synchronization NEW
- Data Maintenance panel NEW
- Synchronized Objects NEW
- Deleted Objects NEW
- DT560 Interface Configuration
- DT561 Configuration Parameters
- DT562 Mapping
- DT563 Load Data Pool
- DT564 Logging
- DT565 Mapping Parameters
- DT566 Employee Pool
- DT567 Project pool
- DT568 System
- DT569 System condition
- DT590 Web interface
- DT592 Web entity
- DT593 Web attribute
- DT594 Web parameter
- DT595 Web request
From DB 39.5.11
General
Workflows (Tutorials)
- Interface Workflow: Export
- Interface Workflow: Import
- Web Interface Workflow: GET
- Web Interface Workflow: PUT
- Web Interface Workflow: POST
- Web Interface Workflow: DELETE
- Interface Configuration
- Configuration and Execution panel
- Interface Administration
- Special Functions
- Web interfaces
- PLANTA pulse interfaces NEW
- Configuration panel NEW
- Data Maintenance panel NEW
- Synchronized Objects NEW
- Deleted Objects NEW
- User Synchronization NEW
- DT560 Interface Configuration
- DT561 Configuration Parameters
- DT562 Mapping
- DT563 Load Data Pool
- DT564 Logging
- DT565 Mapping Parameters
- DT566 Employee Pool
- DT567 Project pool
- DT568 System
- DT569 System condition
- DT590 Web interface
- DT592 Web entity
- DT593 Web attribute
- DT594 Web parameter
- DT595 Web request
From DB 39.5.10
General
Workflows (Tutorials)
- Interface Workflow: Export
- Interface Workflow: Import
- Web Interface Workflow: GET NEW
- Web Interface Workflow: PUT NEW
- Web Interface Workflow: POST NEW
- Web Interface Workflow: DELETE NEW
- Interface Configuration
- Configuration and Execution panel
- Interface Administration
- Special Functions
- Web Interfaces NEW
- Configuration panel NEW
- Web Interfaces NEW
- Web Entities NEW
- Configuration panel NEW
- DT560 Interface Configuration
- DT561 Configuration Parameters
- DT562 Mapping
- DT563 Load Data Pool
- DT564 Logging
- DT565 Mapping Parameters
- DT566 Employee Pool
- DT567 Project pool
- DT568 System
- DT569 System condition
- DT590 Web Interface NEW
- DT592 Web Entity NEW
- DT593 Web Attribute NEW
- DT594 Web Parameter NEW
- DT595 Web Request NEW
From DB 39.5.9
General
Workflows (Tutorials)
Functions
Standard interfaces
Modules
- Interface Configuration NEW
- Configuration and Execution panel NEW
- Interface Administration NEW
- Special functions NEW
From DB 39.5.7
General
Workflows (Tutorials)
Functions
Standard interfaces
Modules
- Configuration panel
- Archive panel
- Administration panel
- Generate Definition NEW
- Systems NEW
- Extended Configuration Options NEW
Up to DB 39.5.7
General
Workflows (Tutorials)
Functions
Standard interfaces
Modules
Data tables
| I | Attachment | History | Size | Date | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
SchnittstellenDrawingQuelle_Ziel.png | r5 r4 r3 r2 r1 | 12.9 K | 2016-02-16 - 19:42 | |
| |
SchnittstellenDrawingQuelle_Ziel.xml | r1 | 2.9 K | 2013-12-17 - 18:22 |